Compounding of Offences Under FEMA Act 1999
Home > Compounding of Offences Under FEMA Act 1999

September 25, 2024
Understanding of FEMA & Compounding of Offences
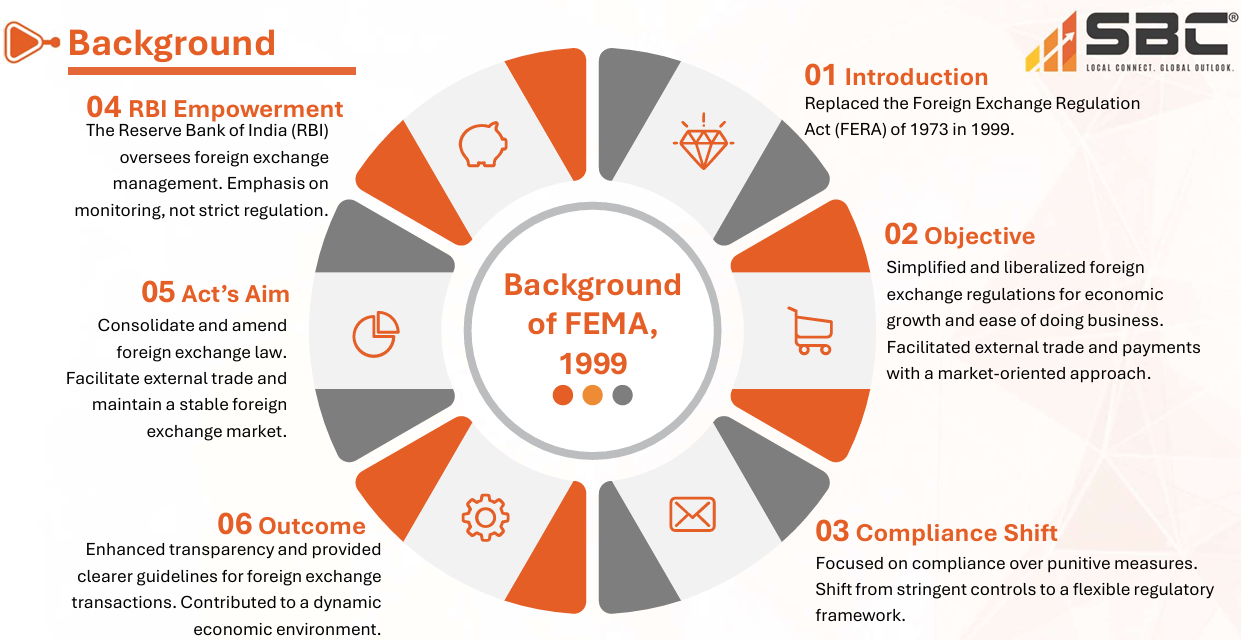
The Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) of 1999 is the primary legislation governing foreign exchange transactions in India, ensuring adherence to international financial regulations. When violations occur, they can lead to penalties or legal actions. However, FEMA permits the compounding of offences, allowing offenders to pay a fee to resolve the violation without facing more severe penalties or prosecution.
The newly introduced Foreign Exchange (Compounding Proceedings) Rules, 2024, update the previous 2000 rules, aiming to streamline the process and improve transparency in handling foreign exchange violations
Compounding Authorities and Their Jurisdiction
The new rules specify that compounding authorities will be from both the Directorate of Enforcement and the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), depending on the type of violation.
1. Director of Enforcement: Acts as the principal authority for compounding violations under Section 3(a) of FEMA, which generally deals with the illegal transfer of foreign exchange and foreign security violations.
2. RBI Officers: RBI officers of various ranks have the authority to compound other contraventions based on the amount involved in the violation:
• Violations under Rs. 60 lakhs: Assistant General Manager or higher.
• Violations under Rs. 2.5 crores: Deputy General Manager or higher.
• Violations under Rs. 5 crores: General Manager or higher.
• Violations above Rs. 5 crores: Chief General Manager or higher.
Compounding Procedures: A Step-by-Step Overview
Users can not only present the presentation on the projector or computer, but they can also print out the presentation.
Application Submission
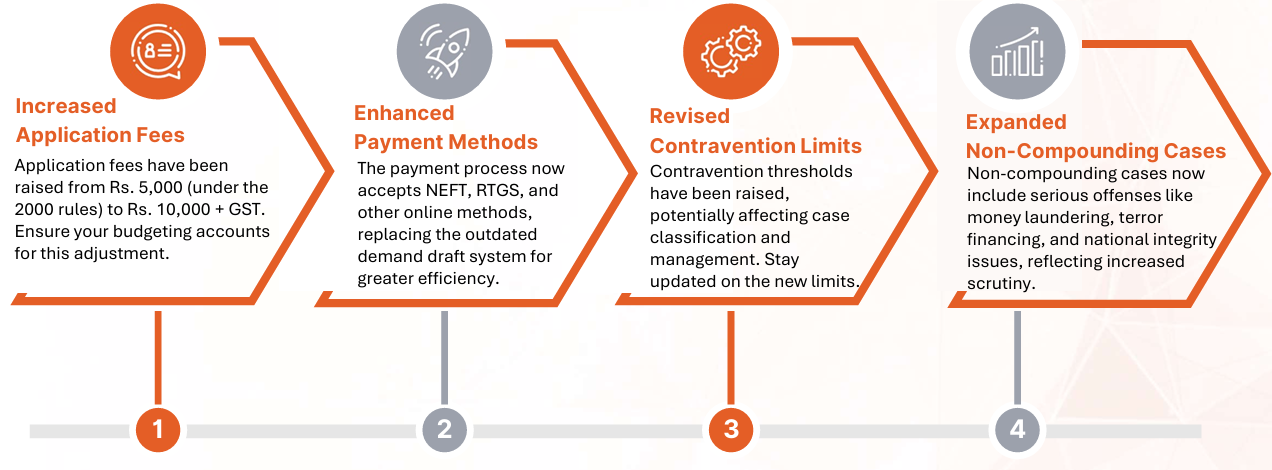
The applicant must submit a compounding application in the prescribed form (detailed in the annexure) to the relevant authority (RBI or Enforcement Directorate), along with a fee of Rs. 10,000 plus applicable Goods and Services Tax (GST).
The payment can be made via Demand Draft, NEFT, RTGS, or other electronic modes.
Evaluation by Compounding Authority
The authority may call for additional information, records, or documents relevant to the case. The applicant may be asked
to furnish further details regarding the transaction involved in the contravention.
Compounding Order
The authority must pass the compounding order within 180 days of receiving the application, ensuring that the case is resolved quickly. The order will include the specific provisions of FEMA violated, details of the contravention, and the amount payable for compounding the offence.
Compounding Procedures: A Step-by-Step Overview
Payment of the Compounded Sum
Once the order is passed, the applicant must pay the compounded sum within 15 days. Failure to make the payment within the stipulated time would mean the application for compounding is void, and the violation would be dealt with as a regular contravention under FEMA.
Discontinuation of Adjudication
If a contravention is compounded before adjudication, any ongoing or pending inquiry related to the violation will be discontinued. Once the compounded sum is paid, the contravention is fully settled, and no further penalties will be imposed.
Issuance of Copy of Compounding Order
A copy of the order is provided to the applicant and the Adjudicating Authority (if involved) to ensure transparency in the
process.
•The application fee has been raised from Rs. 5,000 (as per the 2000 rules) to Rs. 10,000 plus GST.
•Payments can now be made via NEFT, RTGS, and other online methods, moving away from the former demand draft-only requirement
Restrictions on Compounding Certain Offences
Not all FEMA violations are eligible for compounding. The rules specify the following conditions where compounding is not allowed:

Implications of Non-payment and Non-compliance
If the compounded sum is not paid within the specified 15-day period, the application will be nullified and considered as if no compounding application had been submitted. In such situations, the standard provisions of FEMA will take effect, potentially resulting in higher penalties or legal action.
Key Amendments
Verify Email
Verify your email address below to download the PDF