GST Update – 54th GST Council Meeting Recommendations

September 13, 2024
The 54th GST Council
met inter alia made the following recommendations relating to changes in GST tax rates, measures for facilitation of trade and measures for streamlining compliances in GST.
1. List of Services to be added to RCM:
RCM applicability on
a. Renting of commercial property by unregistered to registered person
SBC Comments:
Earlier, w.e.f. 18th July 2022, the renting of residential property was subject to Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM). The proposal now suggests extending RCM to include the renting of commercial property. However, the term “commercial property” has not been explicitly defined in the law. It is also proposed that all types of commercial property rentals may eventually be brought under the purview of GST
b. Supply of Metal scrap by unregistered to registered person
Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) to be introduced on supply of metal scrap by unregistered person to registered person provided that the supplier shall take registration as and when it crosses threshold limit and the recipient who is liable to pay under RCM shall pay tax even if supplier is under threshold.
2. GST TDS on supply of metal scrap:
A TDS of 2% will be applicable on the supply of metal scrap by a registered person in B-to-B supply
SBC Comments:
Previously, the applicability of Tax Deducted at Source (TDS) was restricted to government companies and their related entities. As this metal scrap industry is an unorganized sector. It is now proposed that a 2% TDS will be imposed on the business-to-business (B2B) supply of metal scrap.
3. Proposed GST exemptions

4. Recommendations
a)Introduction of RCM Ledger & IMS
Introduction of a Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) ledger, an Input Tax Credit Reclaim ledger (by 31 October 2024) and an Invoice Management System (IMS)
SBC Comments:
The Reverse Charge Mechanism (RCM) ledger and Invoice Management System (IMS) streamline compliance on the GST portal by allowing to manage of regular ITC and RCM ITC while also providing tools for effective invoice management.
b) Introduction of B2C e-Invoicing
SBC Comments:
B2B E-invoicing compliance was introduced on October 1, 2020. It was mandatory for businesses with a turnover exceeding INR 500 crore or more, which was gradually brought down to INR 5 crore or more. However, due to the large volume of transactions, B2C E invoicing is also being considered. The specific limits for B2C E-invoicing are currently under discussion and will be notified soon.
c) GST on life and health insurance
Constitute a Group of Ministers (GoM) to holistically look into the issues pertaining to GST on life insurance and health insurance. The GoM is to submit the report by end of October 2024.
d) GST on Preferential Location Charges
Location charges or Preferential Location Charges (PLC) paid along with the consideration for the construction services of residential/commercial/industrial complex before issuance of completion certificate forms part of composite supply
SBC Comments:
This clarification comes as a much-needed relief for the real estate industry, addressing the long-standing ambiguity regarding tax rates on Preferential Location Charges (PLC). For buyers, this is great news! Instead of the GST rate of 18% being applied to PLC, it will now be taxed at a reduced rate of 5%, or 1% for affordable housing.
e) Goods Transport Agency (GTA)
When a Goods Transport Agency (GTA) provides additional services (like loading, unloading, packing, unpacking, transshipment, or temporary warehousing) during the transportation of goods by road and issues a consignment note, these services are considered part of a composite supply.
If these services are provided separately and invoiced separately, they are not treated as part of the composite supply of transportation of goods
f) Introduction of sub-sections (5) and (6) into section 16
The GST Council recommended the early notification of sections 118 and 150 of the Finance (No. 2) Act, 2024, which introduce sub-sections (5) and (6) into section 16 of the CGST Act, 2017, with retrospective effect from July 1, 2017. They also suggested a special procedure for rectifying orders under section 148 of the CGST Act for taxable persons who received orders for wrong input tax credit claims but are now eligible under the new sub-sections. Additionally, a circular will be issued to clarify the procedure and address issues related to these new provisions.
SBC Comments:
A retrospective amendment of sub-sections (5) and (6) into section 16 provides great relief to the taxpayers who were affected by delayed claiming of ITC. They can now avail the benefit of it by approaching the appropriated appellate authority for revision of orders.
g) Removal of Rules 96(10), 89(4A), and 89(4B) from the CGST
Rules, 2017
The GST Council recommended that, where the inputs were initially imported without payment of IGST and compensation cess by availing benefits under Notification No. 78/2017-Customs dated 13.10.2017 or Notification No. 79/2017-Customs dated 13.10.2017 are later paid along with interest, the refunded IGST on exports will not breach Rule 96(10) of the CGST Rules. To ease the refund process for exporters, the Council also suggested the prospective removal of Rules 96(10), 89(4A), and 89(4B) from the CGST Rules, 2017.
SBC Comments:
Exporters who fulfill the conditions of paying IGST and compensation cess on imported inputs (along with interest) and having the Bill of Entry reassessed will no longer be required to repay the refunded IGST with interest and penalties under Section 74.
However, many exporters have already incurred penalties, including repayment of the IGST refund, interest, and additional penalties ranging from 15% to 100%.Many taxpayers were unable to claim refunds due to restrictions imposed under Rule 96(10). This is a huge relief given to the exporters with payment of tax.
h) Addition of Rule 164 to the CGST Rules, 2017
The GST Council recommended adding rule 164 to the CGST Rules, 2017, to outline the procedure and conditions for waiving interest or penalties on tax demands for FYs 2017-18, 2018-19, and 2019 20 under section 128A of the CGST Act. They also recommended that the insertion of section 128A (Amnesty Scheme) in CGST Act, 2017, may be notified with effect from 01.11.2024. and related circulars along with
i) The GST Council recommended issuing circulars to clarify and resolve ambiguities on the following issues:
a. Place of Supply for advertising services provided by Indian companies to foreign entities.
b. Availability of Input Tax Credit on demo vehicles for vehicle dealers.
c. Place of Supply for data hosting services provided by Indian service providers to foreign cloud computing service provider
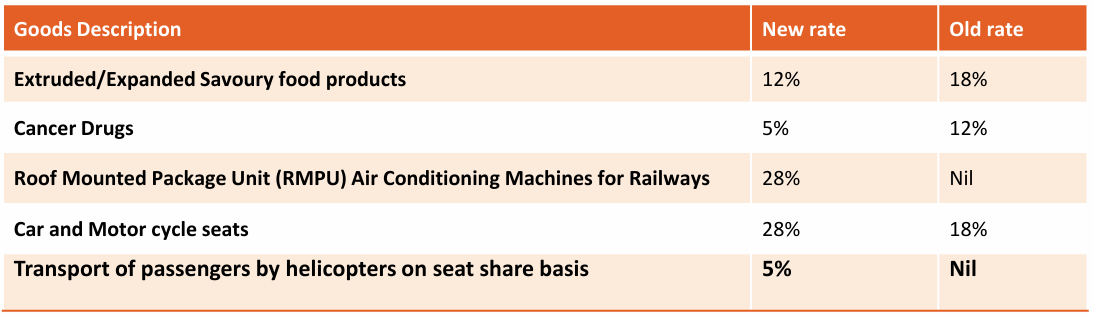
5. Summary of Rate Changes and Exemptions:
Changes in GST Rates on Goods & Services:
Verify Email
Verify your email address below to download the PDF